Greenhouse gas definition Greenhouse gases are the gases which are responsible for causing the greenhouse effect Meaning,How the greenhouse effect functions is a two way process Firstly, being poor absorbers, these gases are unable to prevent the solar radiation that enter the earth's surface This inThe greenhouse effect is a warming of Earth's surface and the air above it It is caused by gases in the air that trap energy from the Sun These heattrapping gases are called greenhouse gases The most common greenhouse gases are water vapor, carbon dioxide, and methane
3
What causes greenhouse gas effect
What causes greenhouse gas effect-Of the six greenhouse gases, three are of primary concern because they're closely associated with human activities Carbon dioxide is the main contributor to climate change, especially through the burning of fossil fuels Methane is produced naturally when vegetation is burned, digested or rotted without oxygen Oil and gas production, cattleGlobal warming is the unusually rapid increase in Earth's average surface temperature over the past century primarily due to the greenhouse gases released as people burn fossil fuels The global average surface temperature rose 06 to 09 degrees Celsius (11 to 16°




Greenhouse Effect Video For Kids The Greenhouse Effect Youtube
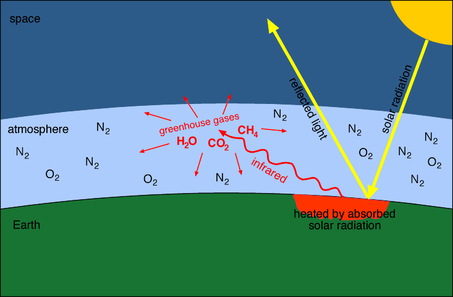
Amplifying the greenhouse effect Like other gases in the atmosphere, including oxygen and nitrogen, greenhouse gases are largely transparent to incoming sunlight Unlike those more abundant gases though, greenhouse gases are not transparent to heat (longwave infrared radiation) The sunwarmed surface of Earth radiates heat day and nightThe greenhouse effect is the process by which radiation from a planet's atmosphere warms the planet's surface to a temperature above what it would be without this atmosphere Radiatively active gases (ie, greenhouse gases) in a planet's atmosphere radiate energy in all directionsThe greenhouse effect is a natural phenomenon and is beneficial for us Certain gases in the atmosphere retain part of the thermal radiation emitted by the Earth's surface after being heated by the sun, this maintains the planet's temperature at a level suitable for the development of life Human action, however, has increased the presence of
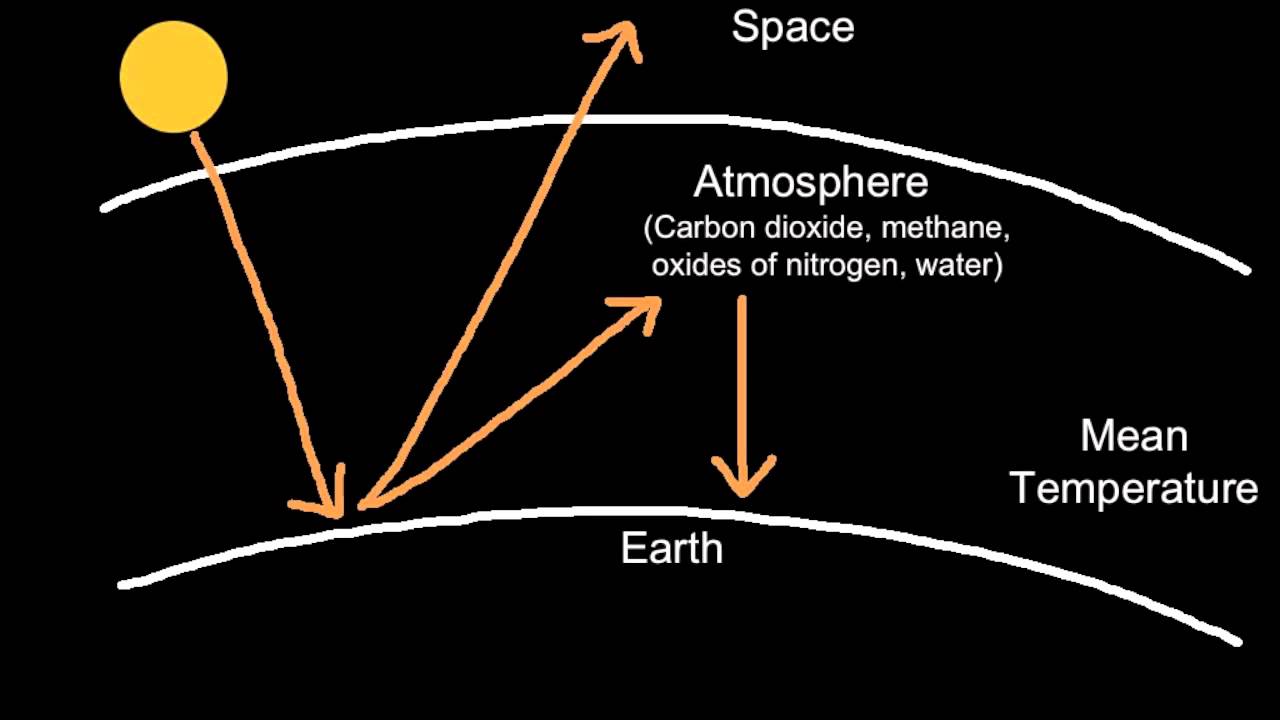
F) between 1906 and 05, and the rate of temperature increase has nearlyThe natural greenhouse effect is a phenomenon caused by gases naturally present in the atmosphere that affect the behaviour of the heat energy radiated by the sun In simple terms, sunlight (shortwave radiation) passes through the atmosphere, and is absorbed by Earth's surfaceGreenhouse effect is a natural process that warms the Earth's surface Water vapor, carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, ozone are greenhouse gases
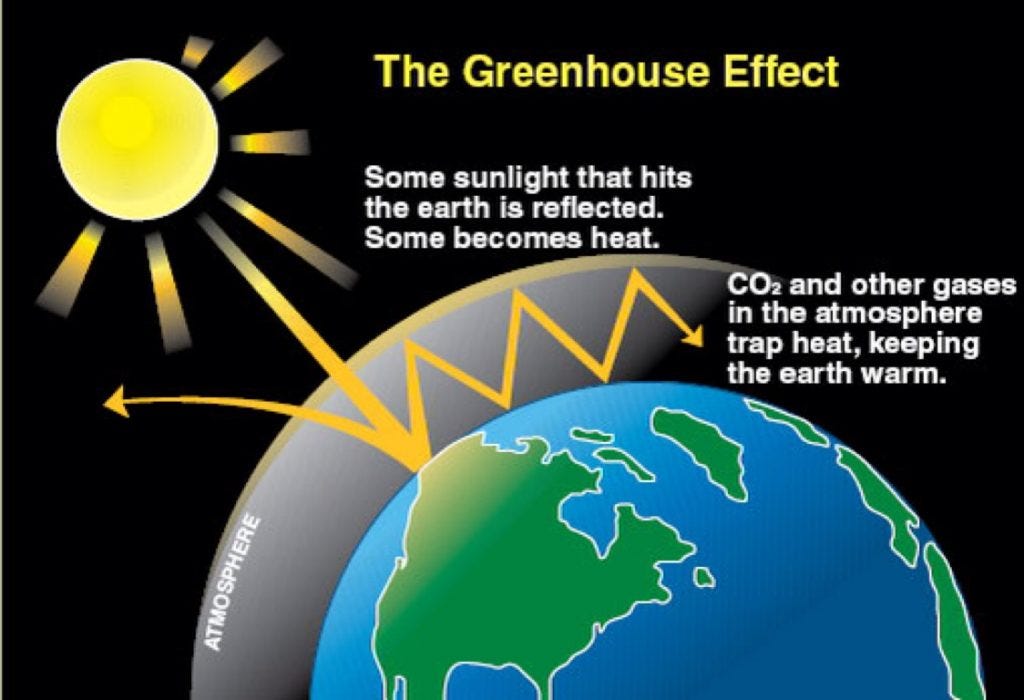
Greenhouse effect – greenhouse gases Our planet receives energy from the Sun in the form of sunlight The Earth's surface absorbs some of this energy and gets warmer That is why the tarmac on a road can still feel hot even after the sun has gone down – because itThe greenhouse effect is a process that occurs when gases in Earth's atmosphere trap the Sun's heat This process makes Earth much warmer than it would be without an atmosphere The greenhouse effect is one of theThe greenhouse effect, in turn, is one of the leading causes of global warming The most significant greenhouse gases, according to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), are water vapor (H2O




Greenhouse Effect 101 Nrdc




Greenhouse Effect
A greenhouse gas is an atmospheric gas that absorbs and emits radiation within the thermal infrared range In other words, it helps keep the planet's surface warm This process is the fundamental cause of the 'greenhouse effect' The greenhouse effect is the natural process by which a planet's atmosphere traps some of its Sun's energyDefine greenhouse gas greenhouse gas synonyms, greenhouse gas pronunciation, greenhouse gas translation, English dictionary definition of greenhouse gas n Any of the atmospheric gases that contribute to the greenhouse effectFor each greenhouse gas, a Global Warming Potential (GWP) has been calculated to reflect how long it remains in the atmosphere, on average, and how strongly it absorbs energy Gases with a higher GWP absorb more energy, per pound, than gases with a lower GWP, and thus contribute more to warming Earth



3




The Greenhouse Effect Climate Matters
The greenhouse effect, combined with increasing levels of greenhouse gases and the resulting global warming, is expected to have profound implications, according to the nearuniversal consensus ofThe greenhouse effect happens when certain gases—known as greenhouse gas es—collect in Earth's atmosphere These gases, which occur naturally in the atmosphere, include carbon dioxide, methane, nitrogen oxide, and fluorinate d gasesThe greenhouse effect keeps the temperatures on our planet mild and suitable for living things Greenhouse gases (GHG) include carbon dioxide, water vapor, methane, ozone, nitrous oxide and fluorinated gases These molecules in our atmosphere are called greenhouse gases



Humans And The Greenhouse Effect Climate Institute




Greenhouse Effect Wikipedia
One of several gases, especially carbon dioxide, that prevent heat from the earth escaping into space, causing the greenhouse effect We need a global system for limiting greenhouse gas emissions Radical steps to reduce greenhouse gases will have a huge effect on the economy" The roots of the greenhouse effect concept lie in the 19th century, when French mathematician Joseph Fourier calculated in 14 that the Earth would be much colder if it had no atmosphere In 16, Swedish scientist Svante Arrhenius was the first to link a rise in carbon dioxide gas from burning fossil fuels with a warming effectA greenhouse gas (GHG or GhG) is a gas that absorbs and emits radiant energy within the thermal infrared range, causing the greenhouse effect The primary greenhouse gases in Earth's atmosphere are water vapor (H 2 O), carbon dioxide (CO 2), methane (CH 4), nitrous oxide (N 2 O), and ozone (O 3)Without greenhouse gases, the average temperature of Earth's surface would




Difference Between Global Warming And Greenhouse Effect Compare The Difference Between Similar Terms




Greenhouse Effect Definition Diagram Causes Facts Britannica
Cause of global warming Almost 100% of the observed temperature increase over the last 50 years has been due to the increase in the atmosphere of greenhouse gas concentrations like water vapour, carbon dioxide (CO 2), methane and ozoneGreenhouse gases are those gases that contribute to the greenhouse effect (see below)The most wellknown greenhouse gas is Carbon Dioxide, also known as CO2 Other greenhouse gases are methane, carbon monoxide, sulphur dioxide, nitrous oxide and water vapourThe "Greenhouse Effect" A greenhouse is a building made of glass that allows sunlight to enter but traps heat inside, so the building stays warm even when it's cold outside Because gases in the Earth's atmosphere also let in light but trap heat, many people call this phenomenon the "greenhouse effect" The greenhouse effect works




Extended Definition The Greenhouse Effect Cleanairdawson




Greenhouse Gas Definition Emissions Greenhouse Effect Britannica
Five Major Greenhouse Gases The most significant gases that cause global warming via the greenhouse effect are the following Carbon Dioxide Accounting for about 76 percent of global humancausedThe greenhouse effect happens when certain gases, which are known as greenhouse gases, accumulate in Earth's atmosphere Greenhouse gases include carbon dioxide (CO 2), methane (CH 4), nitrous oxide (N 2 O), ozone (O 3), and fluorinated gasesIntroduction The enhanced greenhouse effect refers to human activities that are adding to the warming of the atmosphere due to the greenhouse effect —the presence of gases that increases the atmosphere's retention of the heat energy of the sun




What Is The Greenhouse Effect Definition Impact Video Lesson Transcript Study Com




Types Of Greenhouse Gases Definition And Effects On Climate Change
Fluorinated gases (Fgases) are manmade gases that can stay in the atmosphere for centuries and contribute to a global greenhouse effectThere are four types hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs), perfluorocarbons (PFCs), sulfur hexafluoride (SF 6) and nitrogen trifluoride (NF 3)Fgases are a subgroup of the halogenated gases, the majority of which are halocarbons that include fluorine,Greenhouse gas emissions are measured as kilotonnes of carbon dioxide equivalence (CO 2e) This means that the amount of a greenhouse gas that a business emits is measured as an equivalent amount of carbon dioxide which has a global warming potential of one For example, in 15–16, one tonne of methane released into the atmosphere willGreenhouse effect is a concern for students due to the fact that they should know about the pros and cons of certain activities that involve heat radiation beyond the atmospheric level Greenhouse gases have reportedly elevated the mortality rate over the past many years




Implications Of Possible Interpretations Of Greenhouse Gas Balance In The Paris Agreement Philosophical Transactions Of The Royal Society A Mathematical Physical And Engineering Sciences



Climate Science Investigations South Florida Energy The Driver Of Climate
Definition Greenhouse gases are those gaseous constituents of the atmosphere, both natural and anthropogenic, that absorb and emit radiation at specific wavelengths within the spectrum of infrared radiation emitted by the Earth's surface, the atmosphere and clouds This property causes the greenhouse effectTo the enhancement of the natural greenhouse effect This enhanced greenhouse effect has contributed to global warming, an increased rate of warming of the earth's average surface temperature 4 Specifically, increases in GHGs lead to increased absorption of infrared radiation by Earth's atmosphere and warm the lower atmosphereGreenhouse gas emissions from this sector come from direct emissions including fossil fuel combustion for heating and cooking needs, management of waste and wastewater, and leaks from refrigerants in homes and businesses as well as indirect emissions that occur offsite but are associated with use of electricity consumed by homes and businesses




Greenhouse Gas Wikipedia




Greenhouse Gas Emissions Our World In Data
Word forms (plural) greenhouse gases noun ( Extractive engineering General) A greenhouse gas is a gas that contributes to the greenhouse effect by absorbing infrared radiation in the atmosphere Carbon dioxide is considered to be a greenhouse gas because it traps heat radiated into the atmosphere Carbon dioxide is widely considered to beThe greenhouse effect is a natural process that warms the Earth's surface When the Sun's energy reaches the Earth's atmosphere, some of it is reflected back to space and the rest is absorbed and reradiated by greenhouse gasesAny of various gaseous compounds (such as carbon dioxide or methane) that absorb infrared radiation, trap heat in the atmosphere, and contribute to the greenhouse effect Water vapor is an important gas for the study of climate and weather because of its role as a natural greenhouse gas as well as its relationship to clouds and precipitation




What Is Greenhouse Gas Definition Causes Effects Video Lesson Transcript Study Com




Greenhouse Gases A Student S Guide To Global Climate Change Us Epa
Greenhouse Gas (GHG) Reduction As outlined in Executive Order (EO) , Planning for Federal Sustainability in the Next Decade, the goal of reducing greenhouse gas emissions is to minimize the contributions to the greenhouse effect which contributes to global warming and subsequent adverse environmental and human healthGHG reduction is managed by the followingGreenhouse effect definition is warming of the surface and lower atmosphere of a planet (such as Earth or Venus) that is caused by conversion of solar radiation into heat in a process involving selective transmission of short wave solar radiation by the atmosphere, its absorption by the planet's surface, and reradiation as infrared which is absorbed and partly reradiated back to the surface by atmospheric gasesBy increasing the concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, we're amplifying the planet's natural greenhouse effect and turning up the dial on global warming Guide




What Is The Greenhouse Effect Space
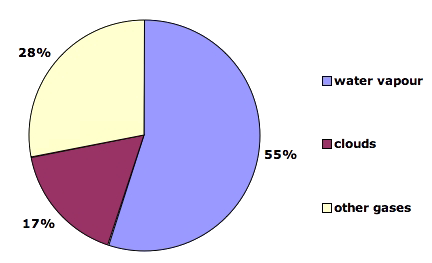



What Gases Are Greenhouse Gases Jean Marc Jancovici
The greenhouse effect is the way in which heat is trapped close to the surface of the Earth by "greenhouse gases" These heattrapping gases can be thought of as a blanket wrapped around the Earth, which keeps it toastier than it would be without them Greenhouse gases include carbon dioxide, methane and nitrous oxidesGreenhouse gases are gases in Earth's atmosphere that trap heat They let sunlight pass through the atmosphere, but they prevent the heat that the sunlight brings from leaving the atmosphere The main greenhouse gases areDefine greenhouse gases greenhouse gases synonyms, greenhouse gases pronunciation, greenhouse gases translation, English dictionary definition of greenhouse gases Carbon dioxide, methane, chlorofluorocarbons, nitrous oxide and lowlevel ozone




Greenhouse Gases Effect On Climate U S Energy Information Administration Eia



Q Tbn And9gcs3 Vn3xnwnq9ifctpyrsa2ofh2ymxfw2rxlcy7frr77uflqr Usqp Cau
Now, over a century later, the mention of greenhouse gas usually evokes thoughts of carbon dioxide (CO 2)That's mainly because changes in the amount of CO 2 in the atmosphere have been linked to the warming of the atmosphere over this past century CO 2 is an important greenhouse gas, and along with water vapor, keeps the Earth warm enough to support life as we know itGreenhouse gas, any gas that has the property of absorbing infrared radiation (net heat energy) emitted from Earth's surface and reradiating it back to Earth's surface, thus contributing to the greenhouse effect Carbon dioxide, methane, and waterGreenhouse gas definition, any of the gases whose absorption of solar radiation is responsible for the greenhouse effect, including carbon dioxide, methane, ozone, and




Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa




Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Definition Solution Facts
Greenhouse gases are responsible for the Greenhouse Effect But before we investigate that, let's find out what greenhouse gases are Can you name any of them?Greenhouse effect, a warming of Earth's surface and troposphere (the lowest layer of the atmosphere) caused by the presence of water vapor, carbon dioxide, methane, and certain other gases in the air Of those gases, known as greenhouse gases,The greenhouse effect is when carbon dioxide and other gases in the Earth's atmosphere capture the Sun's heat radiation Greenhouse gases include CO2, water vapor, methane, nitrous oxide, and ozone




Climate Change Evidence And Causes Royal Society



Greenhouse Gas Wikipedia



The Greenhouse Effect




Greenhouse Gases American Chemical Society




Greenhouse Gas Concentrations In Atmosphere Reach Yet Another High World Meteorological Organization




Greenhouse Gases And The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Video Lesson Transcript Study Com




Greenhouse Gases Causes Sources And Environmental Effects Live Science



5 2 The Greenhouse Effect Bioninja




Esrl Global Monitoring Laboratory Education And Outreach
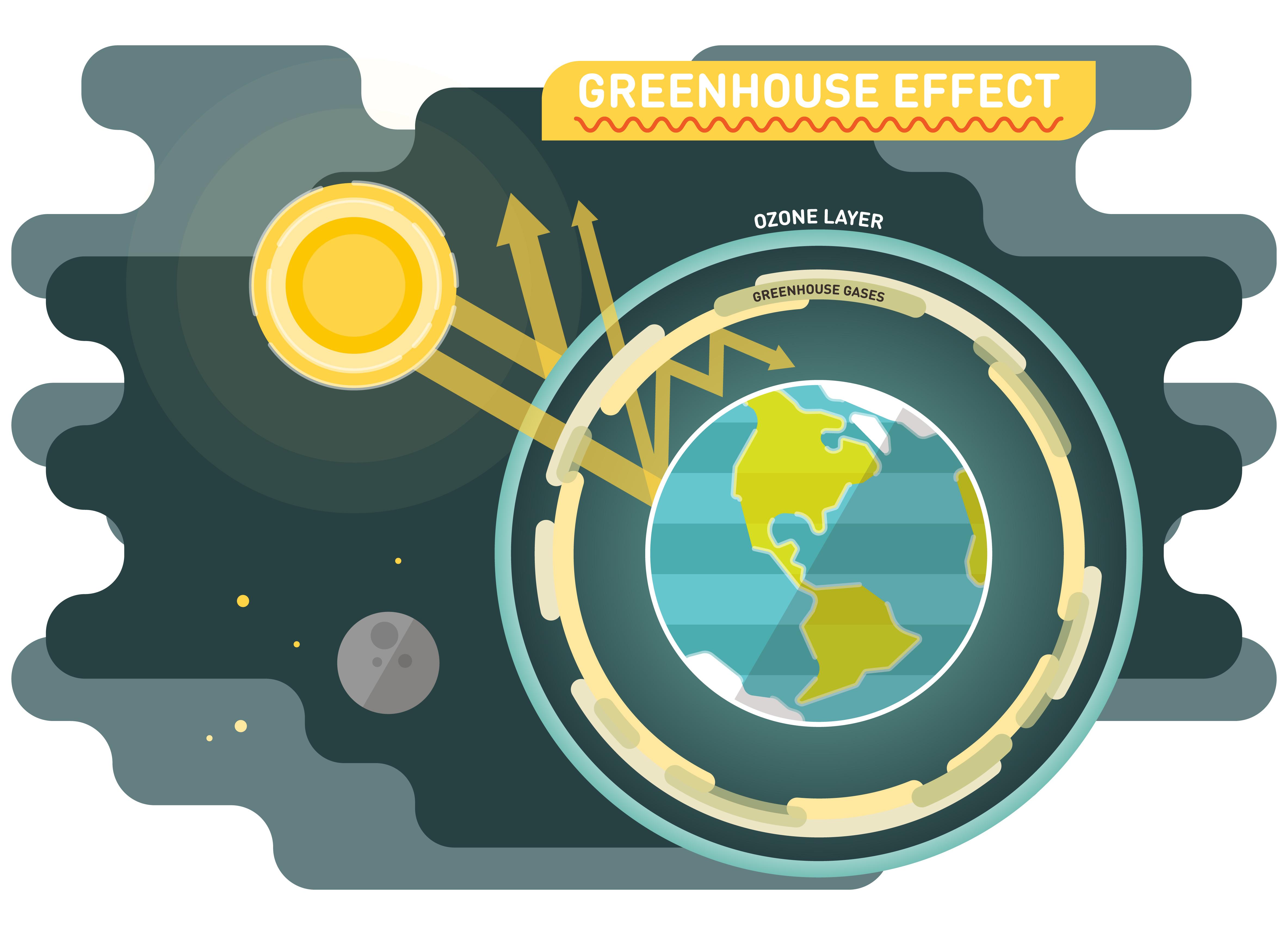



Why The Greenhouse Effect Is Important How It Affects The Climate
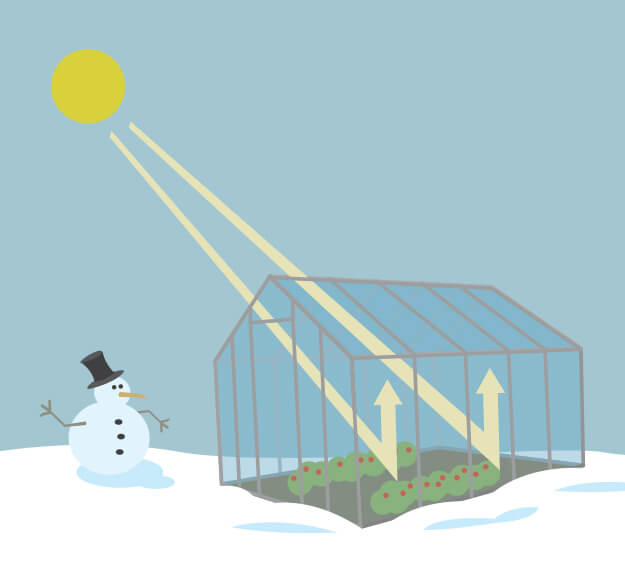




What Is The Greenhouse Effect Nasa Climate Kids




Advantages Or Disadvantages Of The Greenhouse Effect By Maria Mith Medium




Greenhouse Gas Definition Emissions Greenhouse Effect Britannica



1



Untitled Document
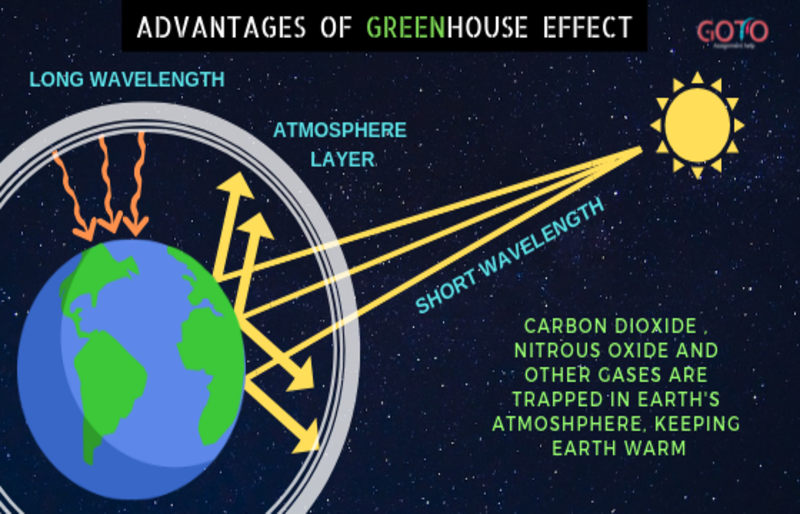



The Advantages Of Greenhouse Effect And The Role Of Greenhouse Gases




Weatherquestions Com What Is The Greenhouse Effect What Are Greenhouse Gases




The Greenhouse Effect Introduction To Chemistry




Greenhouse Effect An Overview Sciencedirect Topics




Greenhouse Effect 101 Nrdc




Greenhouse Gas Definition Emissions Greenhouse Effect Britannica




Runaway Greenhouse Effect Wikipedia




What Is An Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Universe Today




2 Schematic Of The Greenhouse Effect From 16 Download Scientific Diagram




What Is The Greenhouse Effect Nasa Climate Kids




Greenhouse Gas An Overview Sciencedirect Topics




Greenhouse Effect E 3 Pages Definitions 2 Description 3 Greenhouse Gases 4 Greenhouse Gases Effect On Atmosphere Ppt Download




The Greenhouse Effect Presenters Jaime Pinto Nathalie Mokuba Ppt Video Online Download




Pdf Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Gases And Their Impact On Global Warming
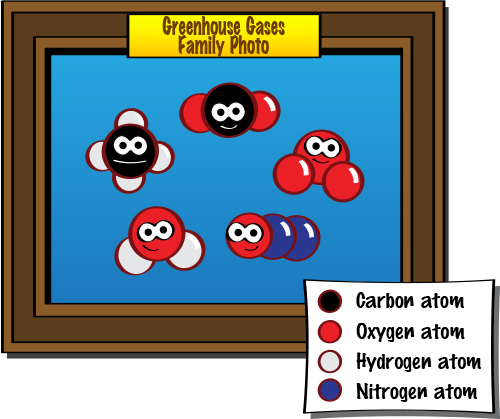



Greenhouse Effect Keeping The Balance Nasa Climate Kids




Greenhouse Gas Definition Emissions Greenhouse Effect Britannica




The Greenhouse Effect British Geological Survey



The Greenhouse Effect
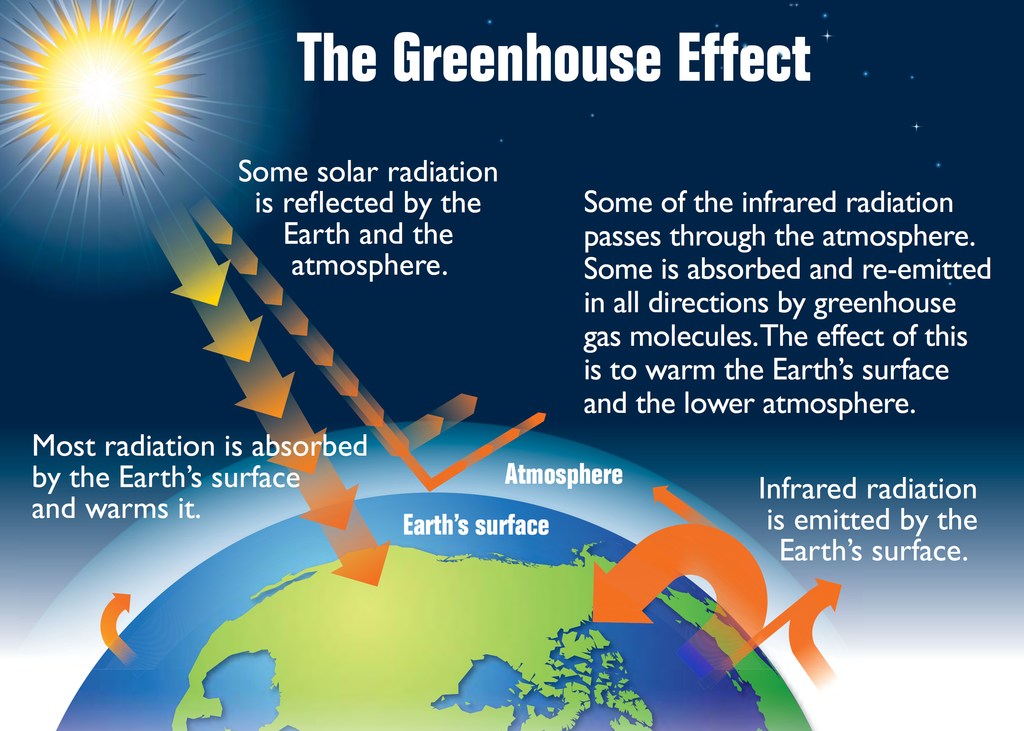



What Is The Greenhouse Effect




Greenhouse Effect Wikipedia




Greenhouse Effect Video For Kids The Greenhouse Effect Youtube




What Is The Greenhouse Effect Nasa Climate Kids




Carbon Dioxide Controls Earth S Temperature
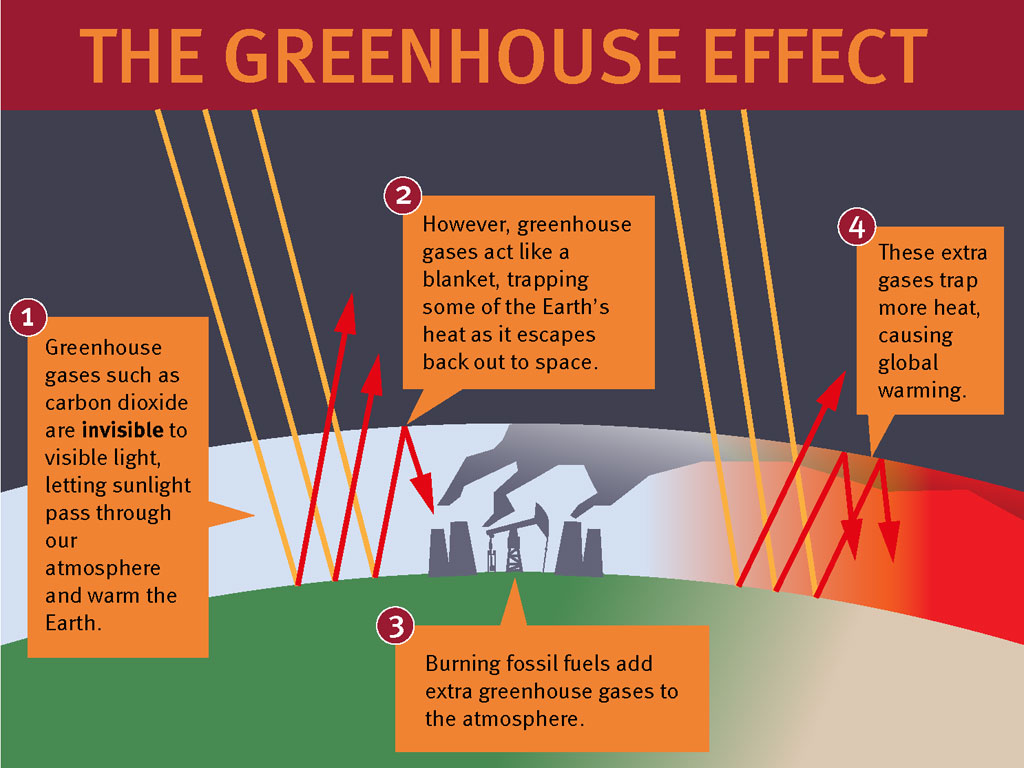



Greenhouse Effect
/GettyImages-474143192-5b7df4fdc9e77c0050c92479.jpg)



Greenhouse Gas Effects On The Economy




Cause And Effect For Global Warming Time For Change
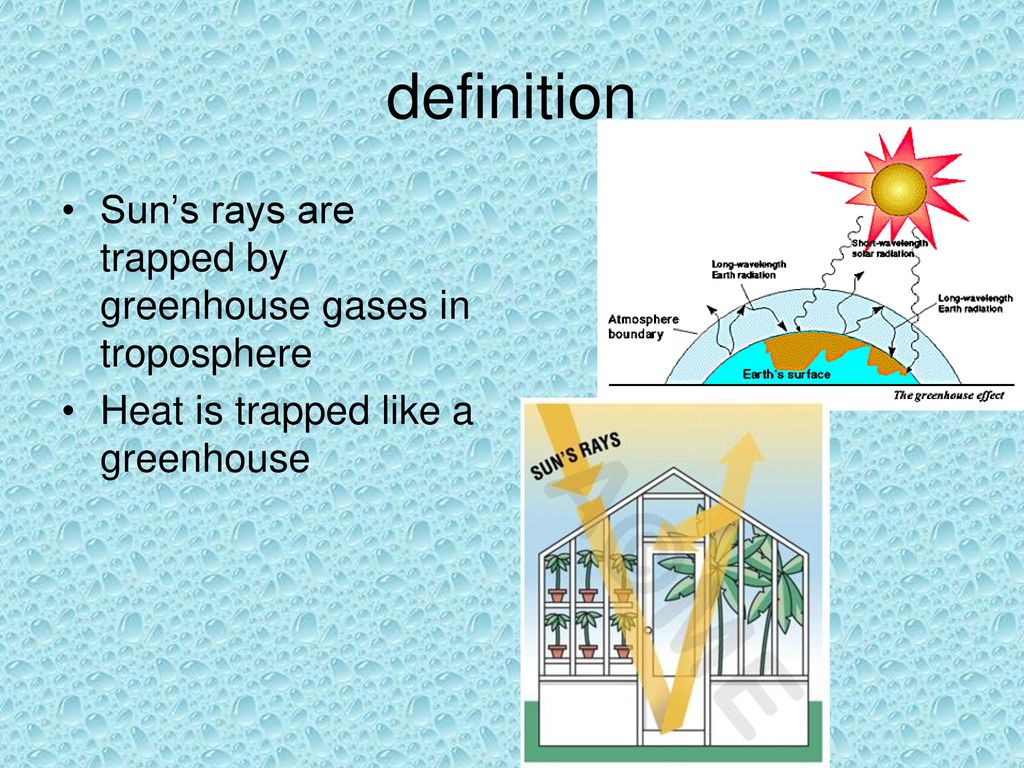



Greenhouse Effect Ppt Download




Greenhouse Effect Kids Britannica Kids Homework Help




Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa



Environment For Kids Global Warming
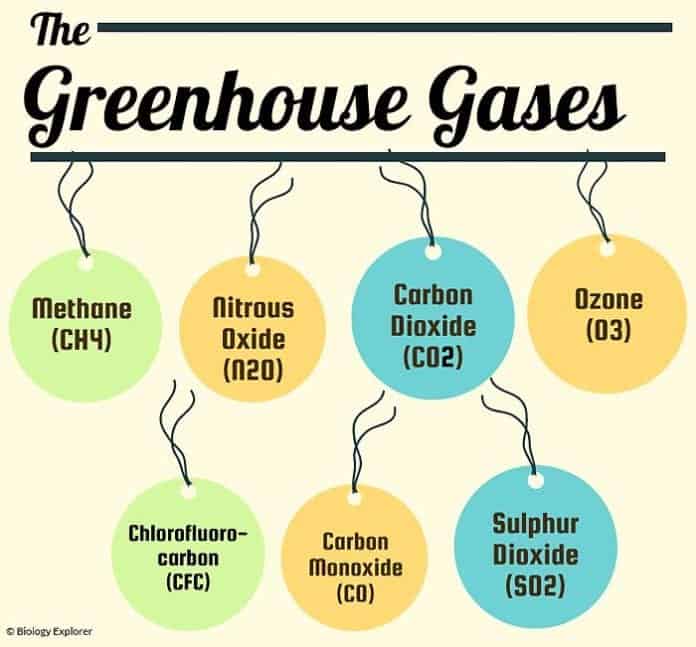



Types Of Greenhouse Gases Definition And Effects On Climate Change




Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa




Pdf The Greenhouse Effect And Its Impacts On Environment




Greenhouse Gases U S Energy Information Administration Eia



Kids Corner



Greenhouse Effect Advantages And Disadvantages By Tutorbin Medium




Co2 The Greenhouse Effect And Global Warming From The Pioneering Work Of Arrhenius And Callendar To Today S Earth System Models Sciencedirect




American English At State What Exactly Is The Greenhouse Effect Find Out With Today S Americanenglish Environmental Awareness Graphic Facebook




Climate Change Climate Change Background The Earth Has Been In A Warming Trend For The Past Few Centuries Mainly Due To The Increase In Greenhouse Ppt Download
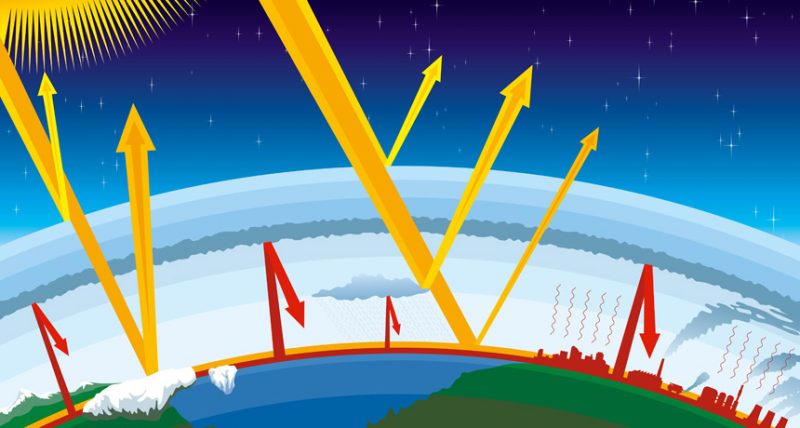




Explainer Global Warming And The Greenhouse Effect Science News For Students




The Greenhouse Effect Explained




The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Ozcoasts




What Is Greenhouse Effect Definition Causes And Effects




The Greenhouse Effect British Geological Survey



Chapter 7 The Greenhouse Effect




The Greenhouse Effect Niwa



1



What Is The Greenhouse Effect Nasa Climate Kids




Greenhouse Effect What Is It Definition And Role In Global Warming




Greenhouse Effect And Global Warming Environmental Science Letstute Youtube




Essay On Greenhouse Effect For Students 500 Words Essay




Carbon Dioxide Methane Nitrous Oxide And The Greenhouse Effect Conservation In A Changing Climate




What Is The Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Live Science



Greenhouse Gases Biology Notes For Igcse 14




Greenhouse Effect Aumsum Kids Science Education Children Youtube




What Is The Greenhouse Effect Lesson For Kids Study Com



Chapter 7 The Greenhouse Effect




Green House Effect Definition Meaning Video For Kids Youtube




Esrl Global Monitoring Laboratory Education And Outreach



Chapter 7 The Greenhouse Effect




Greenhouse Effect Bioninja




Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Effect Definition Greenhouse Effect Define Greenhou Definegreenhou Definitiongre Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Gases Greenhouse




Greenhouse Effect Definition Diagram Causes Facts Britannica




Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa



5 2 3 Explain The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Youtube



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿