Greenhouse gases are gases—like carbon dioxide (CO 2), methane, and nitrous oxide—that keep the Earth warmer than it would be without them The reason they warm the Earth has to do with the way energy enters and leaves our atmosphere When energy from the sun first reaches us, it does so mainly as light Use this web page to find specific data files available from the public ftp file archive of the ESRL Global Monitoring Laboratory Alternatively, you can check our Data by research program page for specific areas of data that can be downloaded Click on the icons ( or ) under the 'Data' table heading in the dataset description boxes to either download the data file desired, orGreenhouse gases come from all sorts of everyday activities, such as using electricity, heating our homes, and driving around town The graph to the right shows which activities produce the most greenhouse gases in the United States These greenhouse gases don't just stay in one place after they're added to the atmosphere
30 Catchy Controlling Greenhouse Gas Slogans List lines Phrases Names 21
Greenhouse gases name methane
Greenhouse gases name methane-Carbon dioxide (CO 2), methane (CH 4), nitrous oxide (N 2 O), Ozone (O 3), and chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs), along with water vapour are known as greenhouse gases Due to human intervention, the amount of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere has increased remarkably causing the greenhouse effect Amplifying the greenhouse effect Like other gases in the atmosphere, including oxygen and nitrogen, greenhouse gases are largely transparent to incoming sunlight Unlike those more abundant gases though, greenhouse gases are not transparent to heat (longwave infrared radiation) The sunwarmed surface of Earth radiates heat day and night
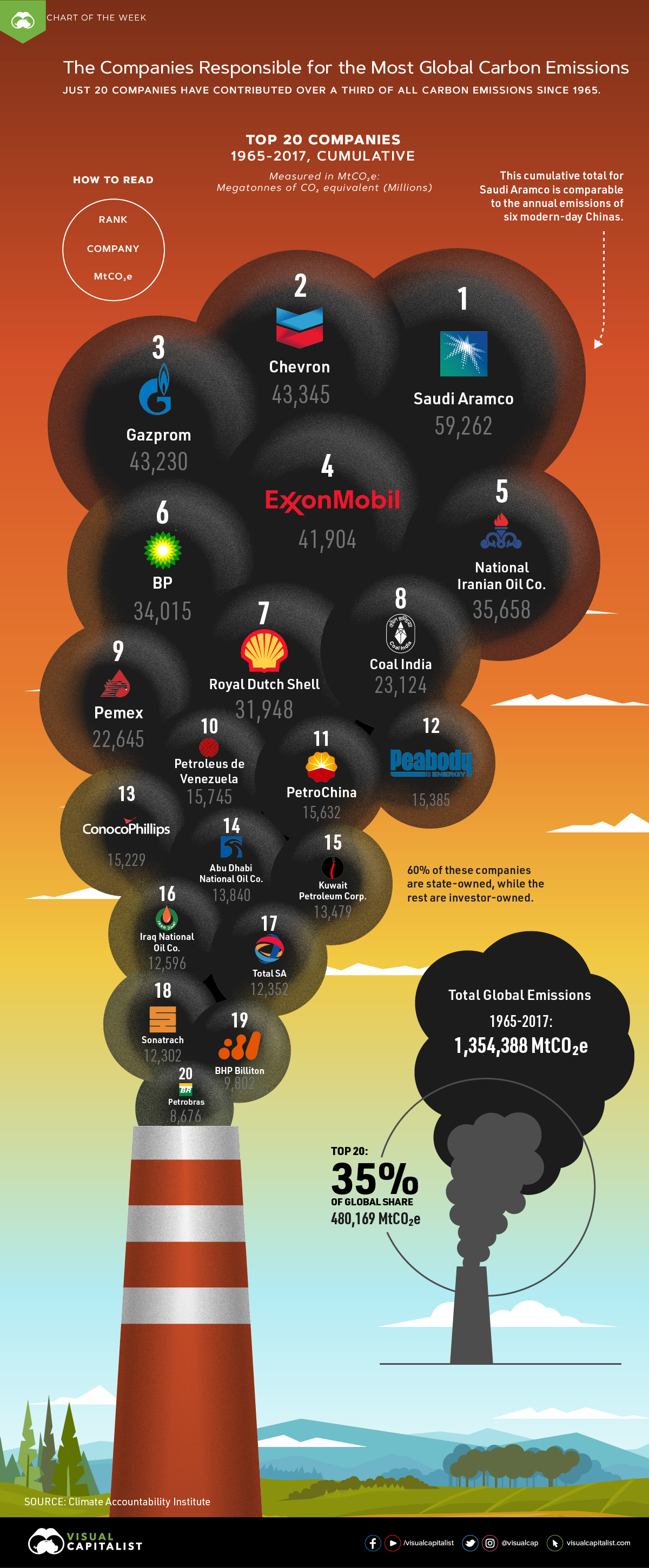



Which Companies Are Responsible For The Most Carbon Emissions
Learners will draw conclusions about the effect of greenhouse gases on temperature and on human life and kinesthetically model the absorbing and reradiation of heat The lesson models scientific inquiry using the 5E instructional model and includes teacher notes, prerequisite concepts, common misconceptions, student journal and reading The greenhouse effect, in turn, is one of the leading causes of global warming The most significant greenhouse gases, according to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), are water vapor (H2OThe Greenhouse is a game about greenhouse gases and our atmosphere The team that survives the longest wins To survive, your team must prevent the Earth Token from reaching the top of the Inspector's Name _____ About how many turns did your group take before the Earth Token reached the top of the
The greenhouse effect is the way in which heat is trapped close to Earth's surface by "greenhouse gases" These heattrapping gases can be thought of as a blanket wrapped around Earth, keeping the planet toastier than it would be without them Greenhouse gases include carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxidesThe term "greenhouse gases," or GHGs, covers a wide variety of gases that, once they are released into the atmosphere, trap the sun's heat When the sun's energy reaches the Earth's atmosphere, some of it is reflected back to space and the rest is absorbed and trapped in the lower atmosphere, heating the EarthGreenhouse gases that occur both naturally and from human activities include water vapor, carbon dioxide (CO 2 ), methane (CH 4 ), nitrous oxide (N 2 O) and ozone (O 3) Other greenhouse gases have essentially no natural sources, but are side products of industrial processes or manufactured for human purposes such as cleaning agents
Greenhouse Gases Gases that trap heat in the atmosphere are called greenhouse gases These include carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide and fluorinated gases Solar radiation in the lower atmosphere acts like a "greenhouse" – thus the name – preventing heat from escaping Emissions of greenhouse gases into the atmosphere is the mainFind 7 ways to say GREENHOUSE, along with antonyms, related words, and example sentences at Thesauruscom, the world's most trusted free thesaurus The greenhouse effect makes our planet's temperature brighter and more favorable to living things Greenhouse gases (GHGs) include carbon dioxide, water vapor, methane, ozone, nitrous oxide, and fluoride gases These molecules in our atmosphere are called greenhouse gases




Greenhouse Gases U S Energy Information Administration Eia




Greenhouse Gases Factsheet Center For Sustainable Systems
They include methane, nitrous oxide, ozone, and halogenated gases Some of these gases make significant contributions to changing the radiation balance of our planet Other important information for understanding the role of greenhouse gases in climate science characteristics of a greenhouse gas greenhouse gasesLet's consider the principal GHGs one at a time, starting with water vapor, the most abundant greenhouse gas in the atmosphere according to NOAA's National Climatic Data Center (NCDC) Water Vapor Carbon Dioxide (CO 2) Methane (CH 4) Nitrous oxide (N 2 O) Fluorinated Gases (HFCs, PFCs, SF 6) References and Resources A greenhouse gas is a gas in the atmosphere that absorbs and emits radiation This is causing a "greenhouse effect", and the resultant warming of the earth's surface to a temperature above its normal temperature range The radiation is released and redirect towards the earth surface depends on a number of greenhouse gasses in the atmosphere




Carbon Dioxide Methane Nitrous Oxide And The Greenhouse Effect Conservation In A Changing Climate




District Wise Total Annual Greenhouse Gas Emissions From Eight Major Download Scientific Diagram
Greenhouse gases are certain molecules in the air that have the ability to trap heat in the Earth's atmosphere Some greenhouse gases, like carbon dioxide (CO 2) and methane (CH 4), occur naturally and play an important role in Earth's climate If they didn't exist, the planet would be a much colder place Greenhouse gases warm the planet Scientists know with virtual certainty that increasing greenhouse gas concentrations tend to warm the planet In computerbased models, rising concentrations of greenhouse gases produce an increase in the average surface temperature of the earth over timeAdditional trace gases produced by industrial activity that have greenhouse properties include nitrous oxide (N 2 O) and fluorinated gases (halocarbons) The latter includes sulfur hexafluoride, hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs), and perfluorocarbons (PFCs)




List Of 10 Human Causes Of Global Warming For Reusethisbag Com




1 A Greenhouse Gases List Major Greenhouse Gases Chegg Com
Carbon dioxide Methane Ozone Nitrous oxide Chlorofluorocarbons Greenhouse gases are gases that can trap heat They get their name from greenhouses A greenhouse is full of windows that let in sunlight That sunlight creates warmthSynonyms for greenhouse gas in Free Thesaurus Antonyms for greenhouse gas 1 synonym for greenhouse gas greenhouse emission What are synonyms for greenhouse gas?Too cold to sustain life on earth But human activities are changing earth's natural greenhouse effect with a dramatic increase in the release of greenhouse gases
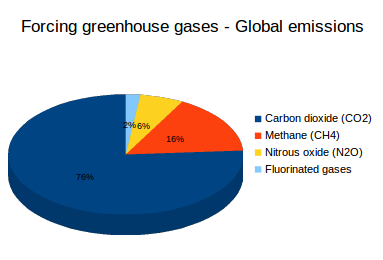



What Are Greenhouse Gases What S Your Impact




Greenhouse Gases A Student S Guide To Global Climate Change Us Epa
Global warming the increase in Earth's average surface temperature due to rising levels of greenhouse gases Climate change a longterm change in the Earth's climate, or of a region on Earth Within scientific journals, this is still how the two terms are used Global warming refers to surface temperature increases, while climate changeIn general, fluorinated gases are the most potent and longest lasting type of greenhouse gases emitted by human activities There are four main categories of fluorinated gases—hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs), perfluorocarbons (PFCs), sulfur hexafluoride (SF 6 ), and nitrogen trifluoride (NF 3 )Synonyms for Greenhouse gases in Free Thesaurus Antonyms for Greenhouse gases 1 synonym for greenhouse gas greenhouse emission What are synonyms for Greenhouse gases?
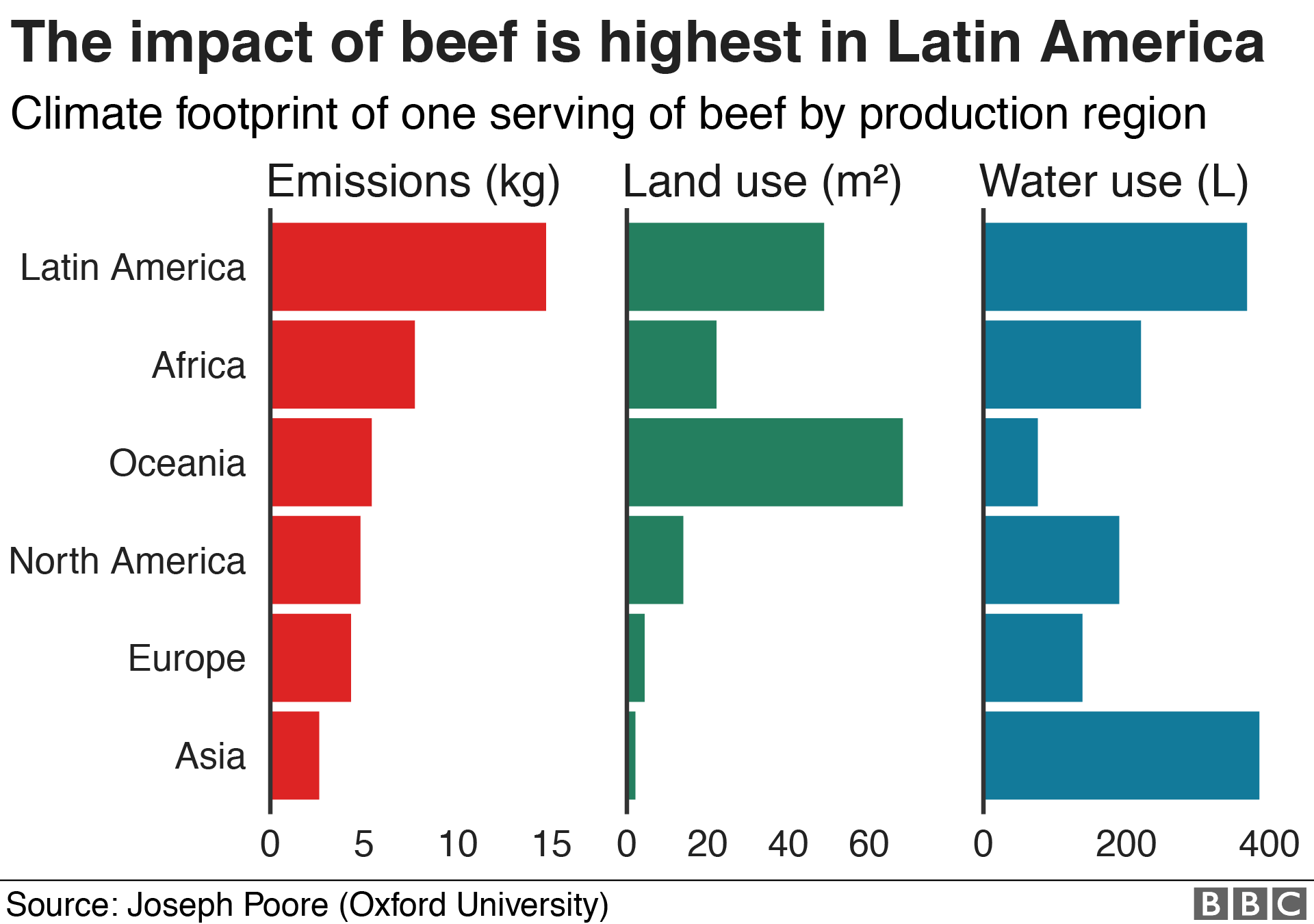



Climate Change Food Calculator What S Your Diet S Carbon Footprint c News




Greenhouse Gas Wikipedia
8 rows Greenhouse gas Chemical formula Global Warming Potential, 100year time horizon Atmospheric The greenhouse effect makes our planet's temperature brighter and more favorable to living things Greenhouse gases (GHGs) include carbon dioxide, water vapor, methane, ozone, nitrous oxide, and fluoride gases These molecules in our atmosphere are called greenhouse gases Carbon dioxide (CO2) Accounts for around threequarters of the warming impact of current human greenhousegas emissions The key source of CO2 is the burning of fossil fuels such as coal, oil and
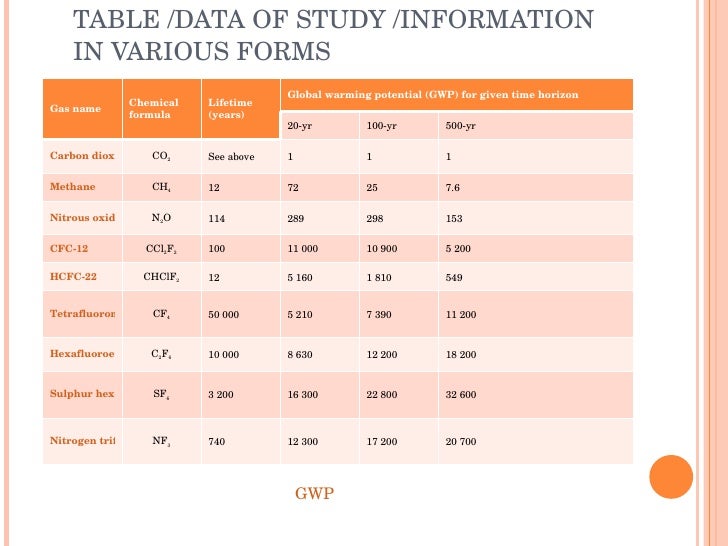



Green House Effect



What Are The Natural Sources Of Greenhouse Gases Quora
The greenhouse effect happens when certain gases—known as greenhouse gases—collect in Earth's atmosphere These gases, which occur naturally in the atmosphere, include carbon dioxide , methane , nitrogen oxide, and fluorinate d gases sometimes known as chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs)A greenhouse gas (GHG) is any gas in the atmosphere that takes in (absorbs) and gives off (emits) radiation in the heat (infrared) wavelength range Greenhouse gases cause the greenhouse effect, which results in increased temperatures on Earth Source National Climatic Data CenterNOAA PaleoclimatologyCarbon dioxide (CO 2) makes up the vast majority of greenhouse gas emissions from the sector, but smaller amounts of methane (CH 4) and nitrous oxide (N 2 O) are also emitted These gases are released during the combustion of fossil fuels, such as coal, oil, and natural gas, to




Greenhouse Gas Emissions Wikipedia



Boycott Of Biggest Greenhouse Gas Companies Financial Support Of Clean Companies Wakeman S White Birch Nursery
Greenhouse Gases Carbon Dioxide, Water Vapor, Nitrous Oxide, Aerosols Share of Global GHG Emissions 15% A jet airliner leaves condensation trails in the sky The trails are formed by soot and water vapor from the plane engines which burn kerosene Reservoir gases make up about 13% of our total greenhouse gas emissions When land is flooded to make a reservoir, and plants and soil collect in the reservoir waters and downstream, this organic Greenhouse gases include carbon dioxide (CO 2), methane (CH 4), nitrous oxide (N 2 O), ozone (O 3), and fluorinated gases Greenhouse gases allow the sun's light to shine onto Earth's surface, and then the gases, such as ozone, trap the heat that reflects back from the surface inside Earth's atmosphere



Q Tbn And9gcrevtfvebbghz5zkkbq1akjhfs4 Gwdrbwpqnmfiixo2oqlgyw8 Usqp Cau




5 Notorious Greenhouse Gases Britannica
Greenhouse gas, any gas that has the property of absorbing infrared radiation (net heat energy) emitted from Earth's surface and reradiating it back to Earth's surface, thus contributing to the greenhouse effect Carbon dioxide, methane, and water vapour are the most important greenhouse gases (To a lesser extent, surfacelevel ozone, nitrous oxides, and fluorinated gases These gases are known as greenhouse gases Below are the most important greenhouse gases that influence Earth's climate system Water vapor (H2O) is the strongest greenhouse gas, and the concentration of this gas is largely controlled by the temperature of the atmosphere As air becomes warmer, it can hold more moisture or water vaporThe gases act like the glass walls of a greenhouse – hence the name, greenhouse gases Without this greenhouse effect, temperatures would drop to as low as 18˚C (04˚F);




Noaa Index Tracks How Greenhouse Gas Pollution Amplified Global Warming In Welcome To Noaa Research




43 Great Heating Company Names Brandongaille Com




Explainer Co2 And Other Greenhouse Gases Science News For Students




Nick Kapur 70 Of Greenhouse Gas Emissions Are Caused By Just 100 Corporations This Map Names And Shames Their Ceos T Co Tvcknacyjt T Co Mwdpuddzcg



Q Tbn And9gcs3 Vn3xnwnq9ifctpyrsa2ofh2ymxfw2rxlcy7frr77uflqr Usqp Cau
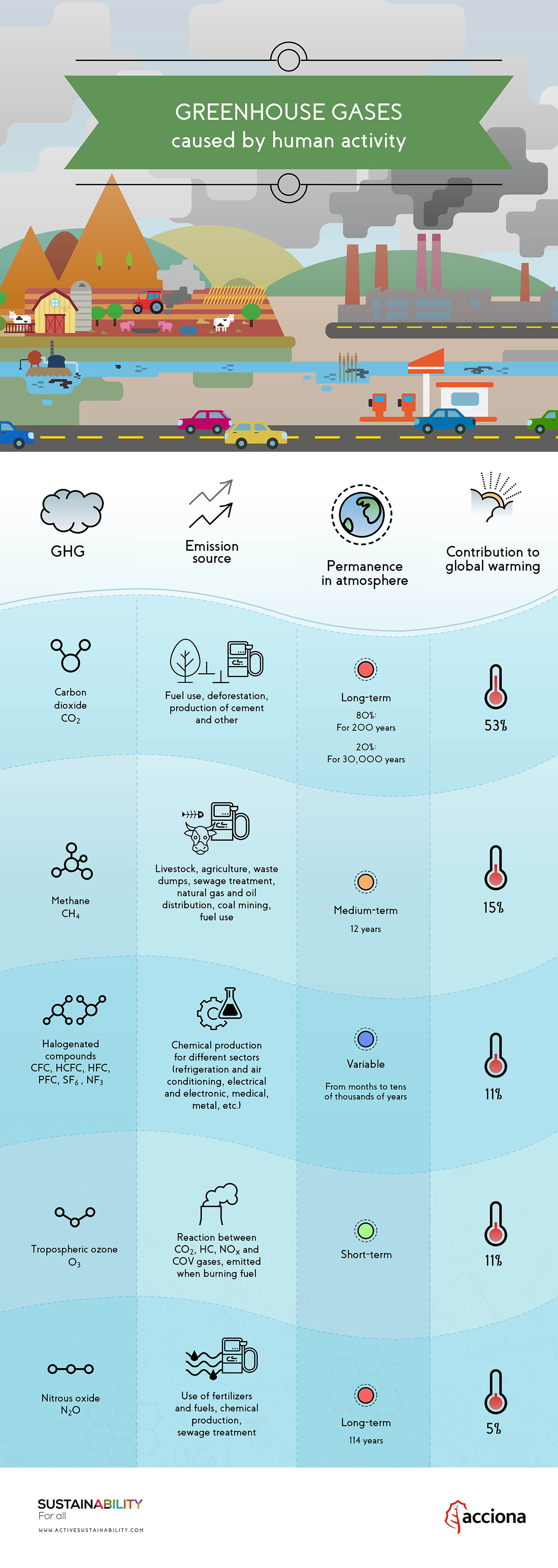



How Do Greenhouse Gases Contribute To Global Warming




Greenhouse Gases Hd Stock Images Shutterstock




Greenhouse Effect 101 Nrdc
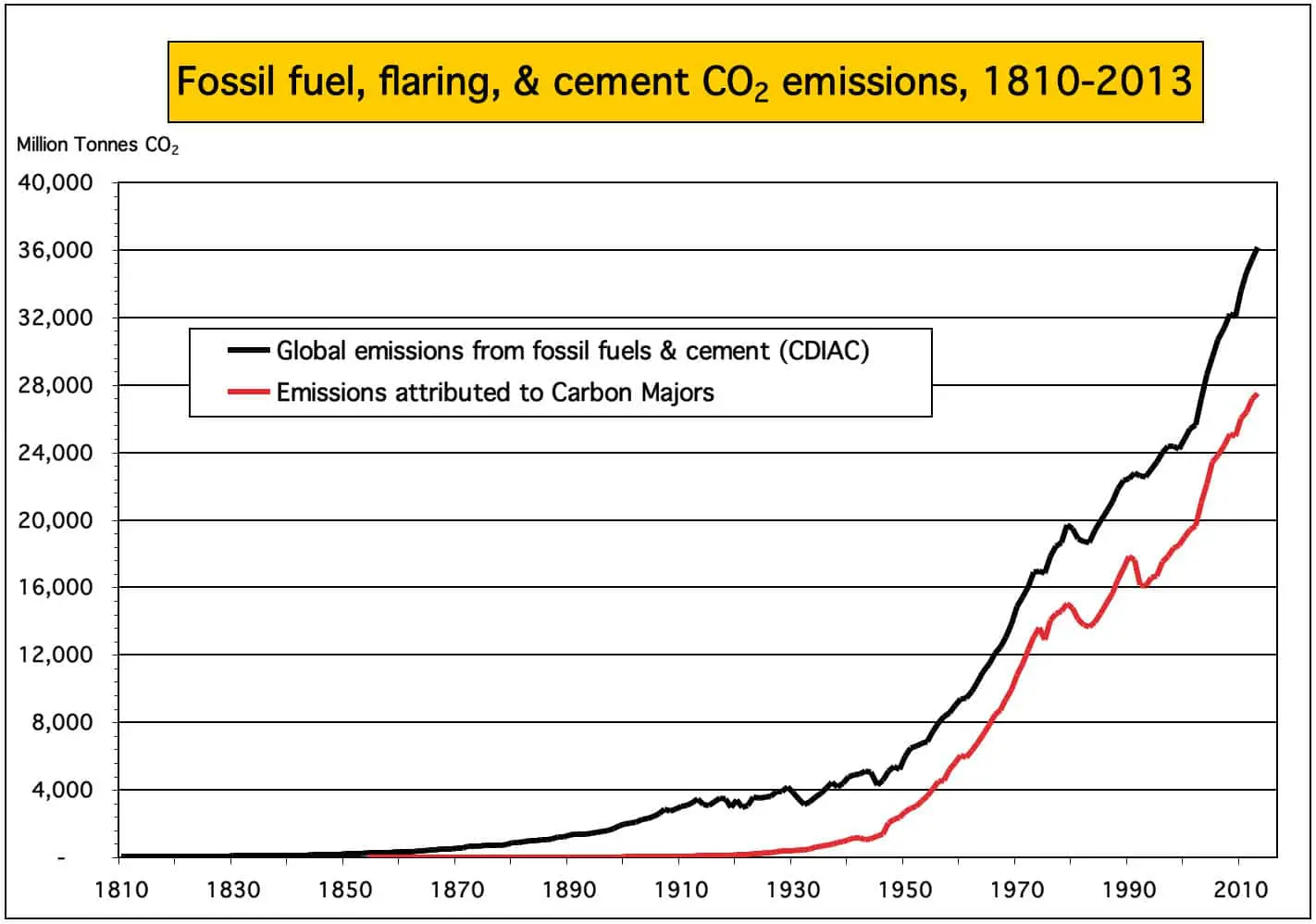



Just 90 Companies Are Accountable For More Than 60 Percent Of Greenhouse Gases Bulletin Of The Atomic Scientists




Greenhouse Gas Wikipedia
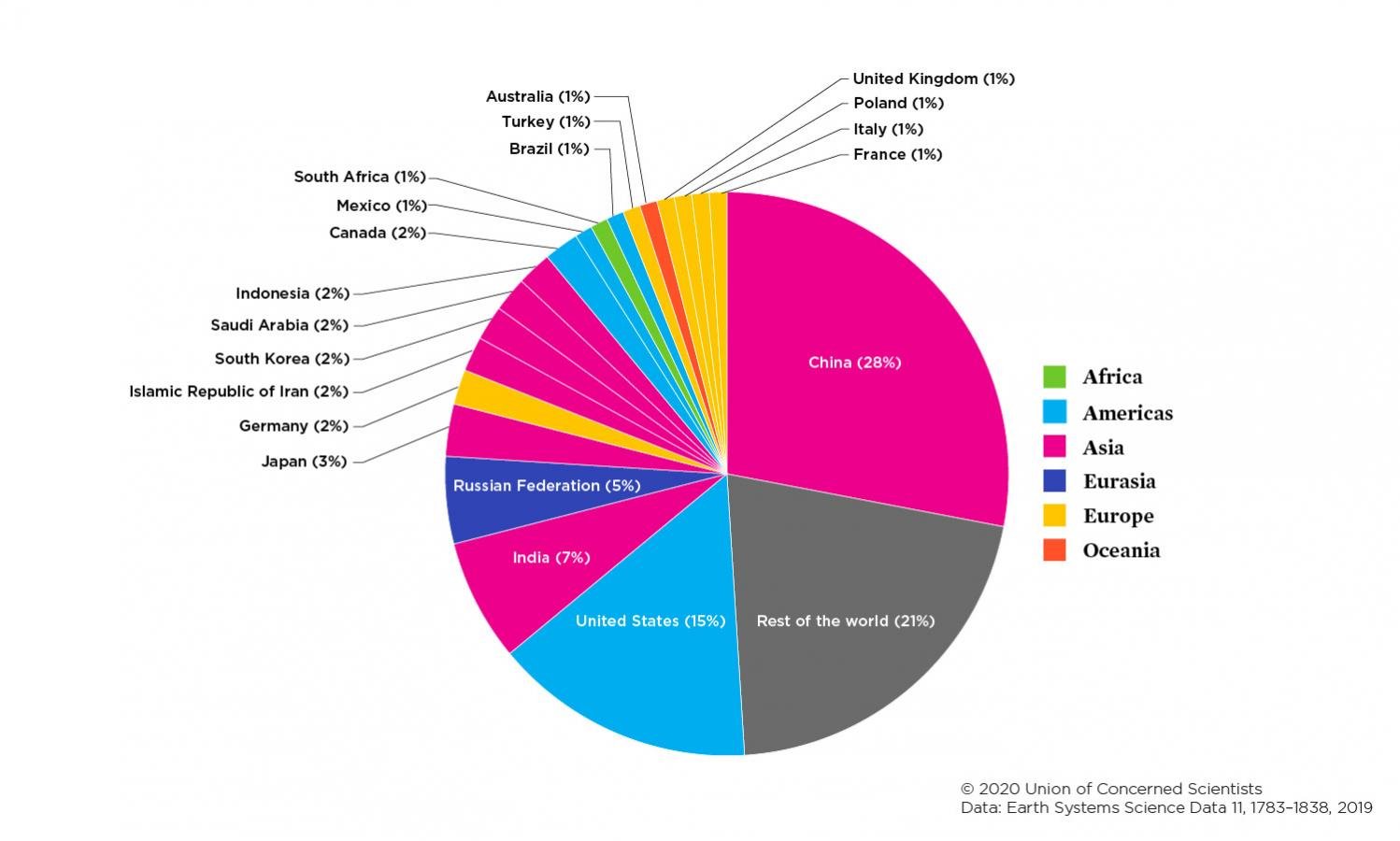



Each Country S Share Of Co2 Emissions Union Of Concerned Scientists




Greenhouse Gases Hd Stock Images Shutterstock




Greenhouse Effect And Greenhouse Gases Greenhouse Ffectffect Ppt Download



What Are The Five Greenhouse Gases Quora




Sources Of Greenhouse Gas Emissions Us Epa



30 Catchy Intro Say On Greenhouse Gases Slogans List lines Phrases Names 21




What Are The Five Greenhouse Gases Quora



30 Catchy Reducing Greenhouse Gas Emissions Slogans List lines Phrases Names 21
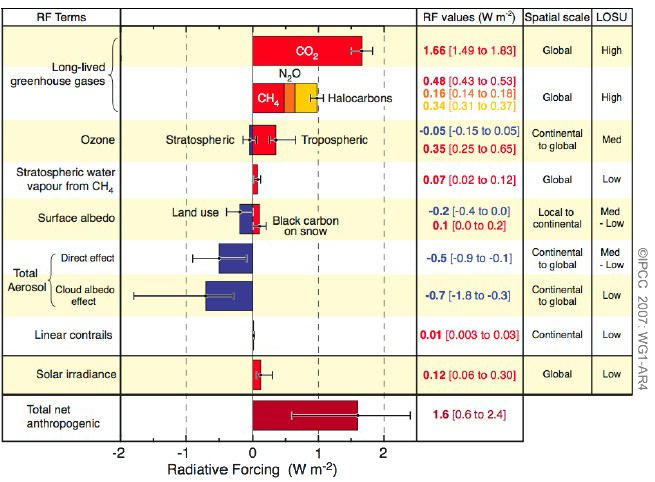



What Gases Are Greenhouse Gases Jean Marc Jancovici




Which Companies Are Responsible For The Most Carbon Emissions
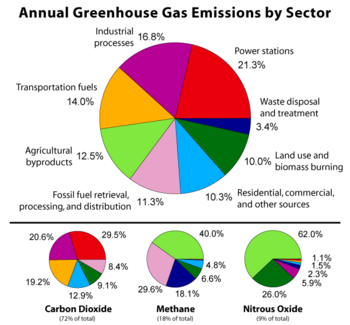



Greenhouse Gas New World Encyclopedia



What Are The Natural Sources Of Greenhouse Gases Quora
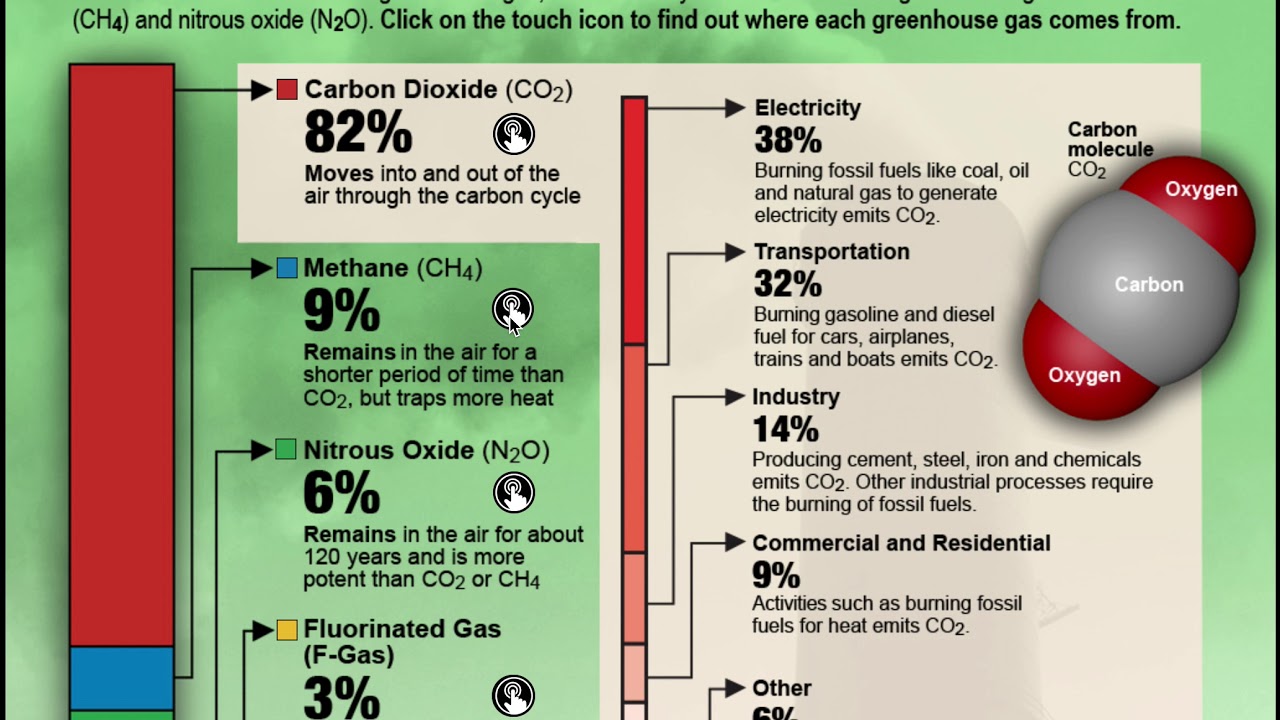



What Are Greenhouse Gases And Where Do They Come From Kqed




Location Of The Existing Greenhouse Gas Measurement Stations In Download Scientific Diagram




Greenhouse Gas Wikipedia




List Of Greenhouse Gases Worldatlas



Climate Change Mitigation Wikipedia
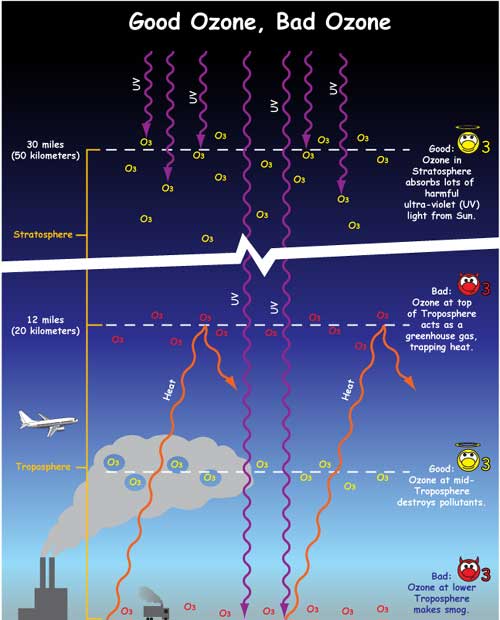



The Greenhouse Effect Nasa Space Place Nasa Science For Kids




Mixed Reaction From Oil Natural Gas Industry As Biden Names Top Climate Energy Picks Natural Gas Intelligence




So What Exactly Is A Feedback Loop Climate Council Greenhouse Gases Feedback Climates




San Antonio S Valero Energy Is The Oil Industry S Fifth Largest Emitter Of Greenhouse Gases The Daily




Researchers Calculate The Greenhouse Gas Value Of Ecosystems Illinois




Greenhouse Effect Take Cornell Notes On This Video Nomk Nomk Ppt Download




Lesson4greenhousegases Climate And Change Edexcel Gcse Geography B




Greenhouse Gas Wikipedia
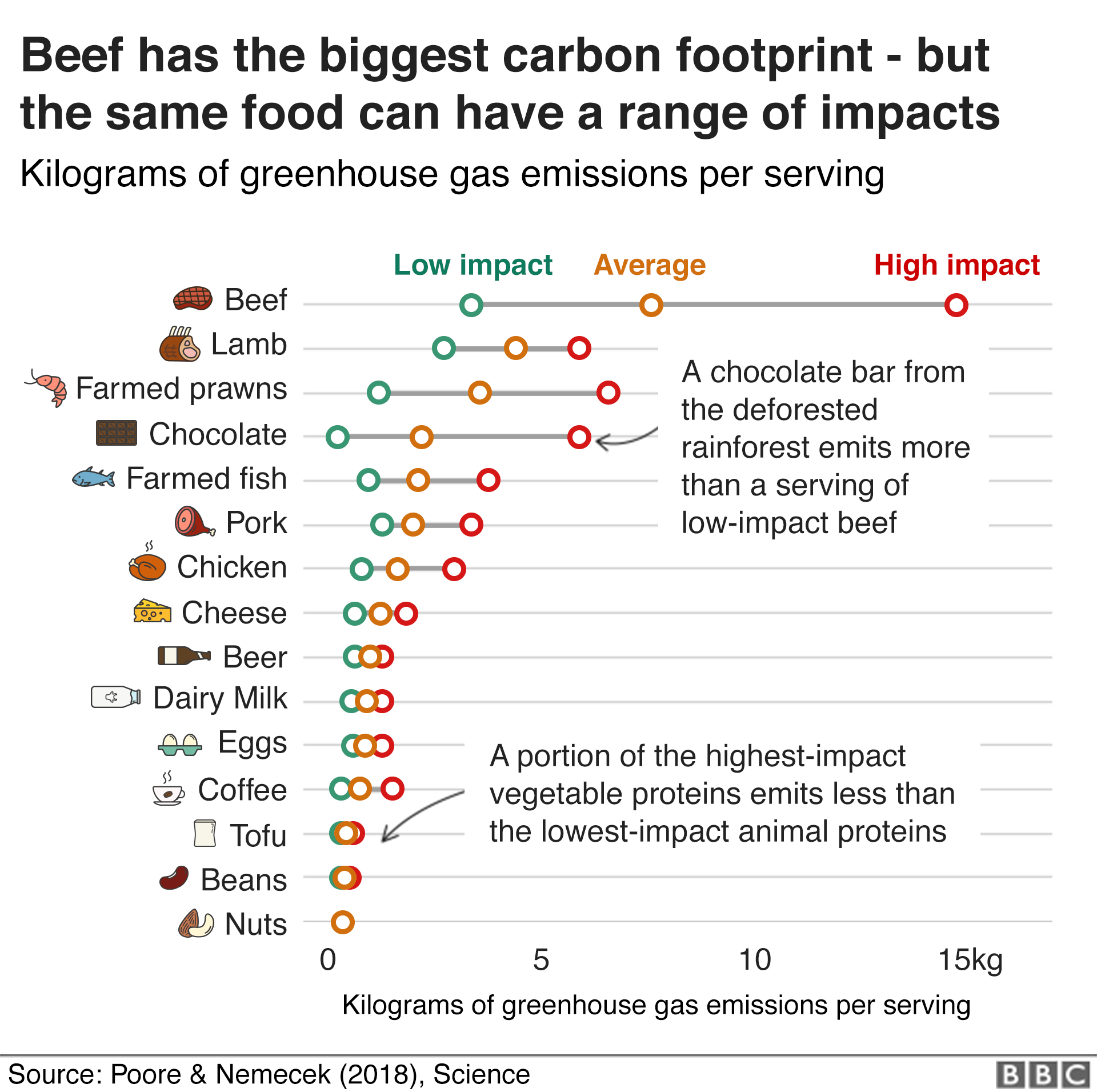



Climate Change Food Calculator What S Your Diet S Carbon Footprint c News



Greenhouse Gases The Environment




Greenhouse Effect Wikipedia
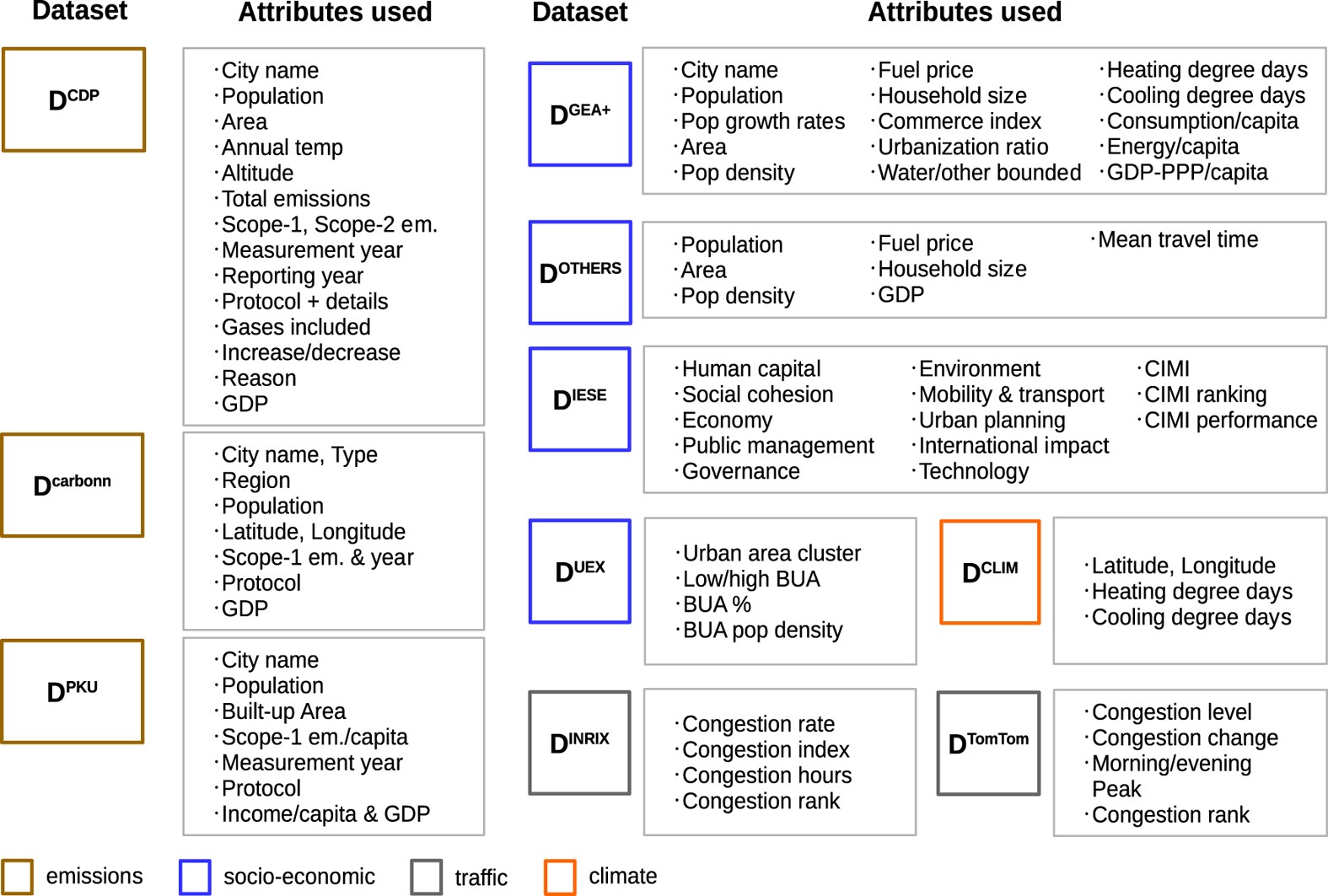



A Global Dataset Of Co2 Emissions And Ancillary Data Related To Emissions For 343 Cities Scientific Data
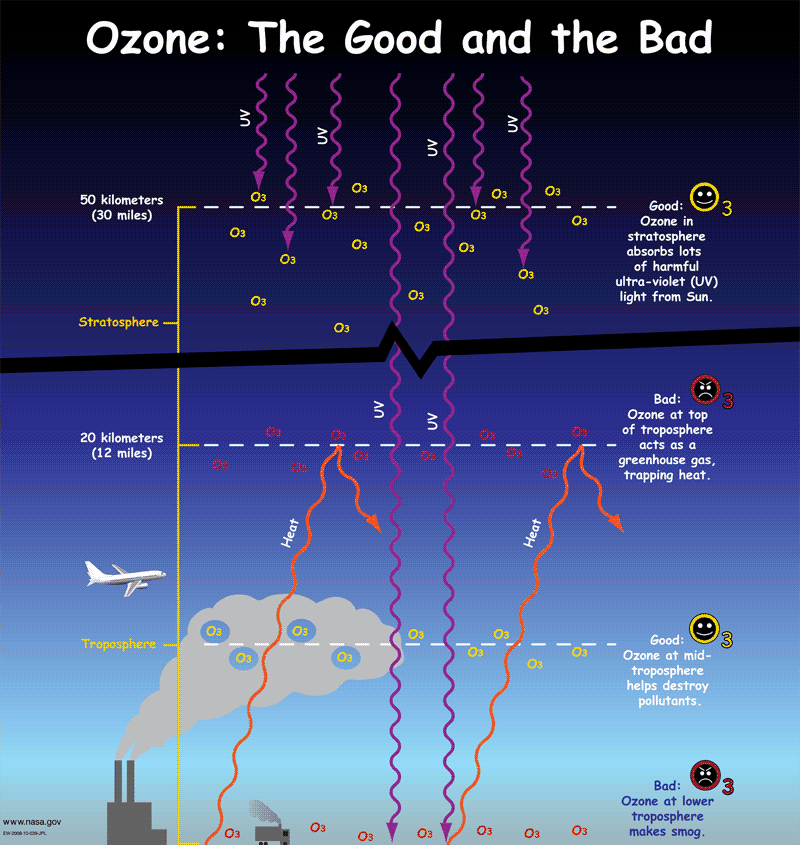



The Greenhouse Effect Nasa Space Place Nasa Science For Kids
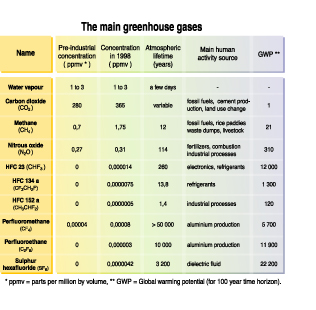



Main Greenhouse Gases Grid Arendal




Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa




Greenhouse Gases Are Rapidly Changing The Atmosphere Climate Central



1




Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa




Greenhouse Gases Science And Technology Wiley Online Library
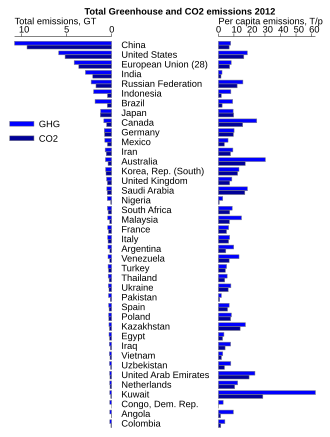



Greenhouse Gas Emissions Wikipedia




The Greenhouse Effect Nasa Space Place Nasa Science For Kids




E 3 2 List The Main Greenhouse Gases Their Sources And Discuss Their Relative Effects Youtube




8 List 5 Trace Gases That Have Been Associated With Chegg Com



30 Catchy Greenhouse Gases Slogans List lines Phrases Names 21




Image Result For Molecules And Atoms Greenhouse Gases Chemistry Lessons Chemical Science




Greenhouse Effect 101 Nrdc
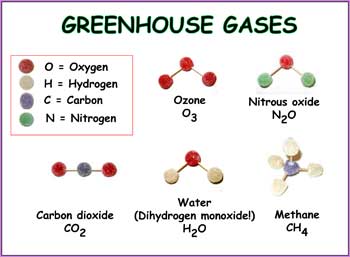



Get Your Gummy Greenhouse Gases Nasa Space Place Nasa Science For Kids




5 Notorious Greenhouse Gases Britannica



30 Catchy Controlling Greenhouse Gas Slogans List lines Phrases Names 21




District Wise Annual Greenhouse Gas Emissions From Crops Livestock And Download Scientific Diagram




Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa




Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa



Climate Science Investigations South Florida Energy The Driver Of Climate




E 3 2 List The Main Greenhouse Gases And Their Sources And Discuss Their Relative Effects Youtube




Types Of Greenhouse Gases Definition And Effects On Climate Change




Lesson Ppt Download
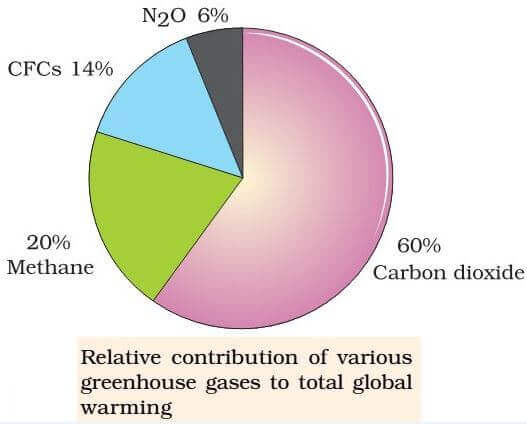



Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Carbon Sequestration Pmf Ias
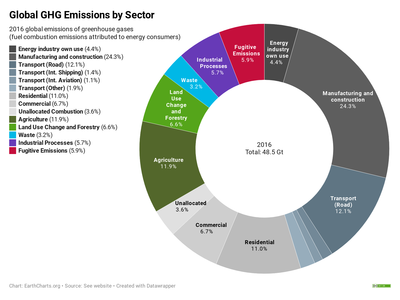



Greenhouse Gas Emissions Wikipedia




Cows Methane And Climate Change Let S Talk Science




Greenhouse Gases A Student S Guide To Global Climate Change Us Epa




A Map Of Noaa Sampling Locations For Greenhouse Gases Used For Download Scientific Diagram
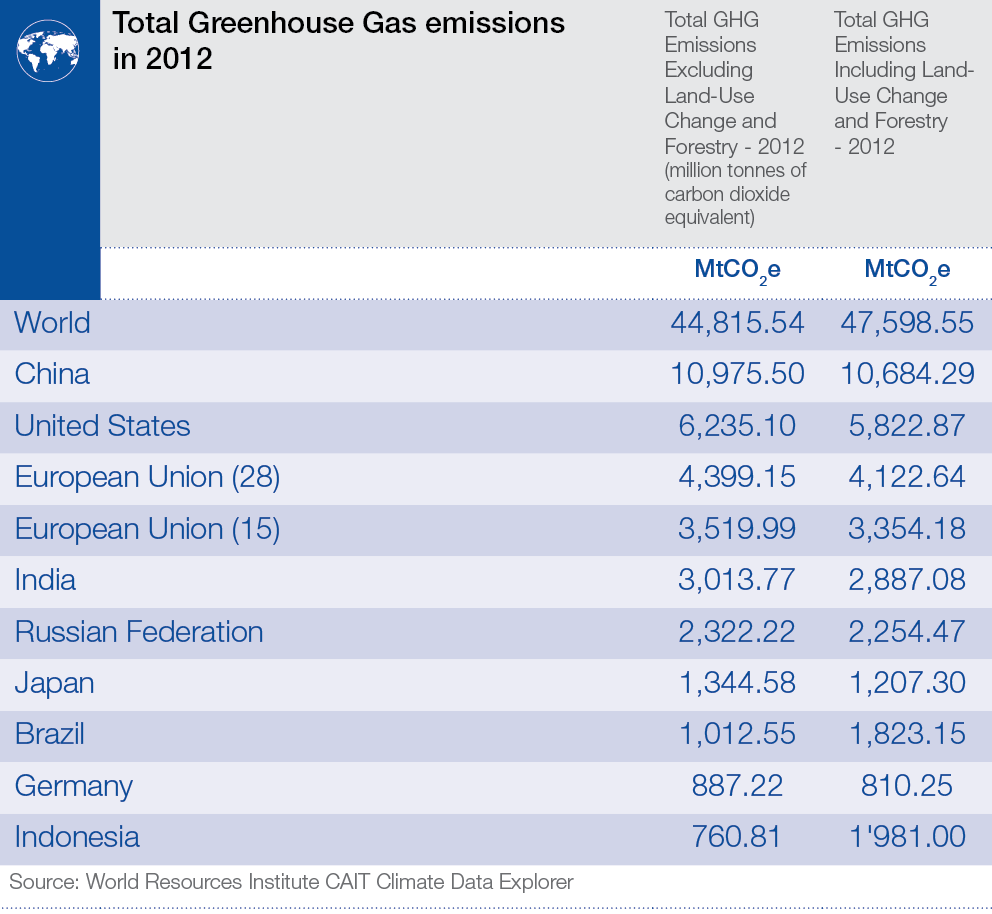



Which Countries Emit The Most Greenhouse Gas World Economic Forum
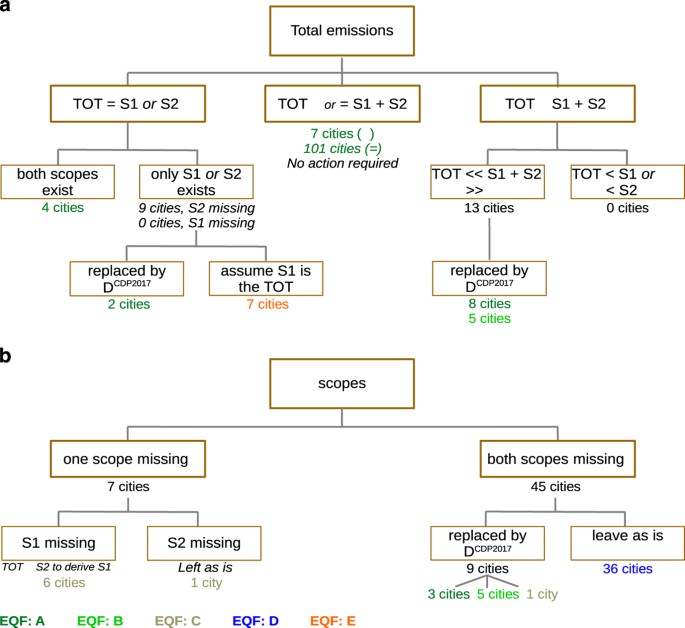



A Global Dataset Of Co2 Emissions And Ancillary Data Related To Emissions For 343 Cities Scientific Data
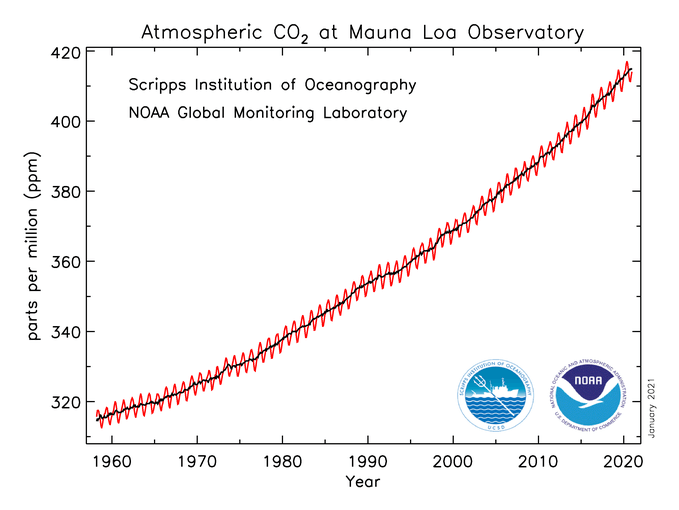



Main Greenhouse Gases Center For Climate And Energy Solutions




List Of 10 Human Causes Of Global Warming For Reusethisbag Com



30 Catchy Funny On Greenhouse Gases Slogans List lines Phrases Names 21



Time Series Of Representative Concentration Pathways Rcp Of Greenhouse Download Scientific Diagram




Greenhouse Effect Definition Diagram Causes Facts Britannica




Which Gases Are Greenhouse Gases American Chemical Society



Q Tbn And9gcrzcnvavdxpfcy 6emwgu68k Cpismnapt0frk Uehnjqqnaxwn Usqp Cau




Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa
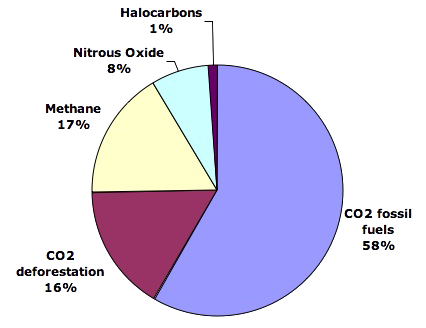



What Gases Are Greenhouse Gases Jean Marc Jancovici




Greenhouse Gas Wikipedia
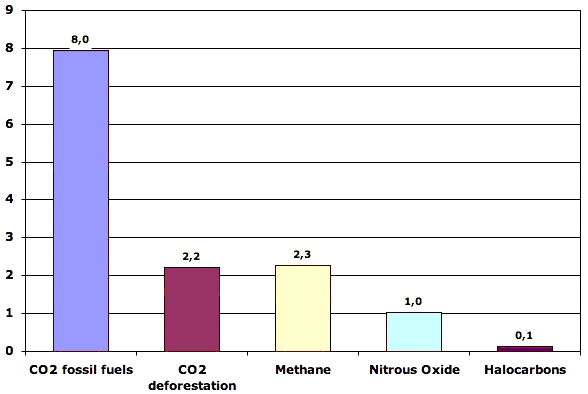



What Gases Are Greenhouse Gases Jean Marc Jancovici
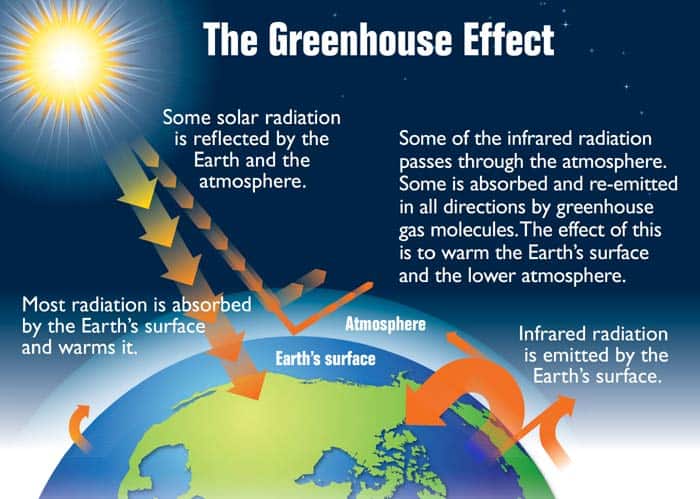



Types Of Greenhouse Gases Definition And Effects On Climate Change




Greenhouse Gases Science And Technology Wiley Online Library
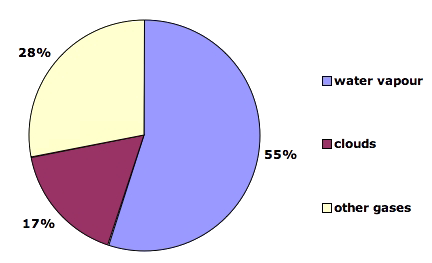



What Gases Are Greenhouse Gases Jean Marc Jancovici




Greenhouse Gas Definition Emissions Greenhouse Effect Britannica




Name The Major Greenhouse Gases And Their Sources Brainly In



80 Environment Vocabulary Environment Words List English Vocabs



30 Catchy Greenhouse Gas Slogans List lines Phrases Names 21



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿